Configuring SNMP
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is used for monitoring appliances in a network. It consists of two entities, namely, an agent and a manager that work in a client-server mode. The manager performs the role of the server and agent acts as the client. Managers collect and process information about the network provided by the client. For more information about SNMP, refer to the following link.
In Protegrity appliances, you can use this protocol to query the performance figures of an appliance. Typically, the ESA acts as a manager that monitors other appliances or Linux systems on the network. In ESA, the SNMP can be used in the following two methods:
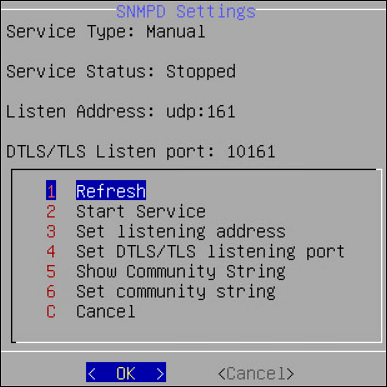
snmpd: The snmpd is an agent that waits for and responds to requests sent by the SNMP manager. The requests are processed, the necessary information is collected, the requested operation is performed, and the results are sent to the manager. You can run basic SNMP commands, such as, snmpstart, snmpget, snmpwalk, snmpsync, and so on. In a typical scenario, an ESA monitors and requests a status report from another appliance on the network, such as, DSG or ESA. By default, the snmpd requests are communicated over the UDP port 161.
In the Appliance CLI Manager, navigate to Networking > SNMP Configuration > Protegrity SNMPD Settings to configure the snmpd settings. The snmpd.conf file in the /etc/snmp directory contains the configuration settings of the SNMP service.
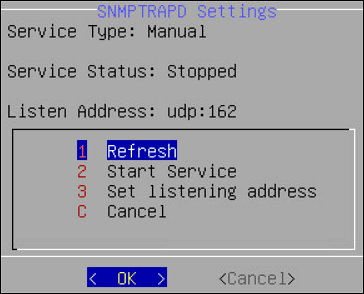
snmptrapd: The snmptrapd is a service that sends messages to the manager in the form of traps. The SNMP traps are alert messages that are configured in the manager in a way that an event occurring at the client immediately triggers a report to the manager. In a typical scenario, you can create a trap in ESA to cold-start a system on the network in case of a power issue. By default, the snmptrapd requests are sent over the UDP port 162. Unlike snmpd, in the snmptrapd service, the agent proactively sends reports to the manager based on the traps that are configured.
In the CLI Manager, navigate to Networking > SNMP Configuration > Protegrity SNMPTRAPD Settings to configure the snmptrapd settings. The snmptrapd.conf file in the /etc/snmp directory can be edited to configure SNMP traps on ESA.
The following table describes the different settings that you configure for snmpd and snmptrapd services.
| Setting | Description | Applicable to SNMPD | Applicable to SNMPTRAPD | Notes |
| Managing service | Start, stop, or restart the service | ✓ | ✓ | Ensure that the SNMP service is running. On the Web UI, navigate to System → Services tab to check the status of the service. |
| Set listening address | Set the port to accept SNMP requests | ✓ | ✓ |
NoteYou can change the listening address only
once. |
| Set DTLS/TLS listening port | Configure SNMP on DTLS over UDP or SNMP on TLS over TCP | ✓ | The default listening port for SNMPD is set to
TCP 10161. | |
| Set community string | String comprising of user id and password to access the statistics of another device | ✓ |
The SNMPv1 is used as default a protocol, but you can also configure SNMPv2 and SNMPv3 to monitor the status and collect information from network devices. The SNMPv3 protocol supports the following two security models:
- User Security Model (USM)
- Transport Security Model (TSM)
Feedback
Was this page helpful?